include를 활용하면 조금더 깔끔하게 조건문을 쓸 수 있다.
function isAnimal(text) {
return (
text === '고양이' || text === '개' || text === '거북이' || text === '너구리'
);
}
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // falsefunction isAnimal(name) {
const animals = ['고양이', '개', '거북이', '너구리'];
return animals.includes(name);
}
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false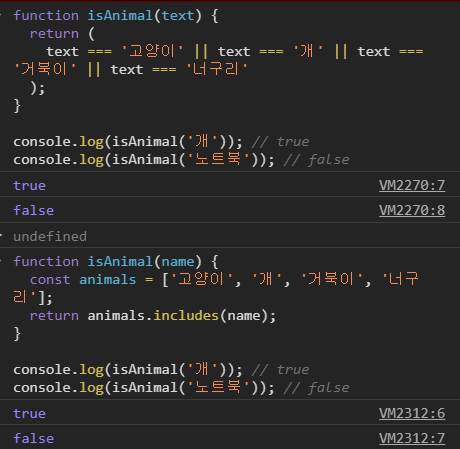
const isAnimal = name => ['고양이', '개', '거북이', '너구리'].includes(name);
console.log(isAnimal('개')); // true
console.log(isAnimal('노트북')); // false화살표 함수로도 활용가능
주어진 값에 따라 다른 결과물을 반환해야 할 때
function getSound(animal) {
if (animal === '개') return '멍멍!';
if (animal === '고양이') return '야옹~';
if (animal === '참새') return '짹짹';
if (animal === '비둘기') return '구구 구 구';
return '...?';
}
console.log(getSound('개')); // 멍멍!
console.log(getSound('비둘기')); // 구구 구 구function getSound(animal) {
const sounds = {
개: '멍멍!',
고양이: '야옹~',
참새: '짹짹',
비둘기: '구구 구 구'
};
return sounds[animal] || '...?';
}
console.log(getSound('개')); // 멍멍!
console.log(getSound('비둘기')); // 구구 구 구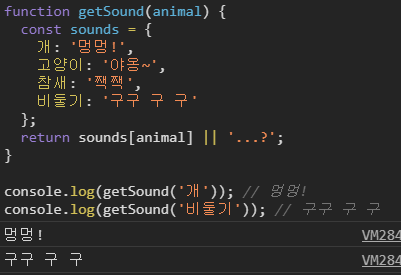
코드 구문이 다를때
function makeSound(animal) {
const tasks = {
개() {
console.log('멍멍');
},
고양이() {
console.log('고양이');
},
비둘기() {
console.log('구구 구 구');
}
};
if (!tasks[animal]) {
console.log('...?');
return;
}
tasks[animal]();
}
makeSound('개');
makeSound('비둘기');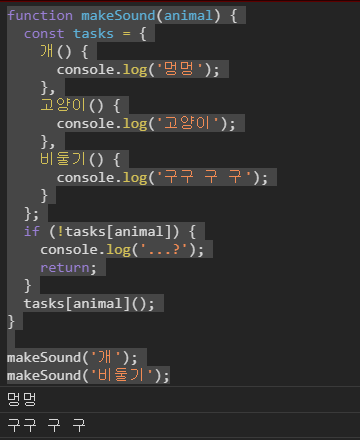
반응형
'JavaScript > javascript 기초 공부하기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| spread, rest 문법 (0) | 2020.01.25 |
|---|---|
| 비구조화 할당(구조분해) (0) | 2020.01.24 |
| Truty and falsy, 단축 평가 논리 계산 (0) | 2020.01.24 |
| 프로토타입과 클래스 (0) | 2020.01.24 |
| 자바스크립트 내장 함수 정리 (forEach, map, indexOf, findIndex, find, filter, splice, slice, concat, join, reduce) (1) | 2020.01.19 |



