타입 단언
as 키워드를 통해 타입을 지정하면 타입스크립트 단에서 특별히 타입을 체크하지 않고 데이터의 구조도 신경쓰지 않는다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="hello">
</div>
</body>
</html>
const hello = document.querySelector('.hello') as HTMLDivElement;
타입가드
interface Developer{
name: string;
skill: string;
}
interface Person{
name: string;
age: number;
}
function introduce(): Developer | Person{
return {name:'Hello', age:33, skill :"Cooking"}
}
const hello = introduce();
console.log(hello.skill)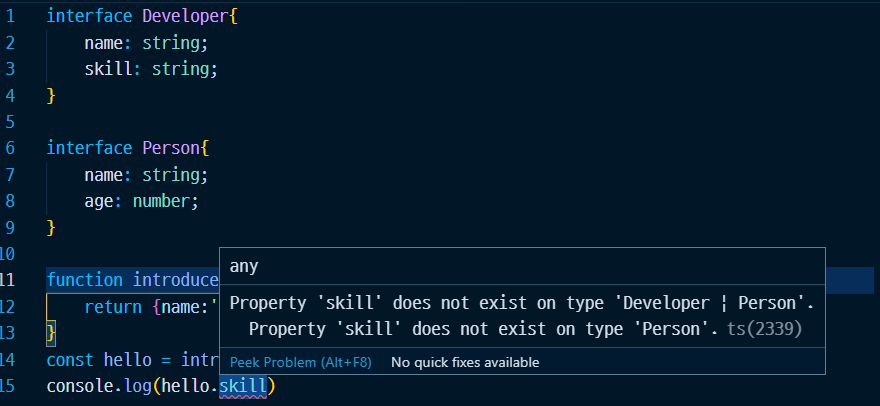
기본적으로 유니온 타입을 사용하게 되면 공통된 속성만 접근 할 수 있게 된다.
interface Developer{
name: string;
skill: string;
}
interface Person{
name: string;
age: number;
}
function introduce(): Developer | Person{
return {name:'Hello', age:33, skill :"Cooking"}
}
const hello = introduce();
console.log(hello.skill);
if((hello as Developer).skill){
const skill = (hello as Developer).skill;
console.log(skill);
}else if((hello as Person).age) {
const age = (hello as Person).age;
console.log(age);
}
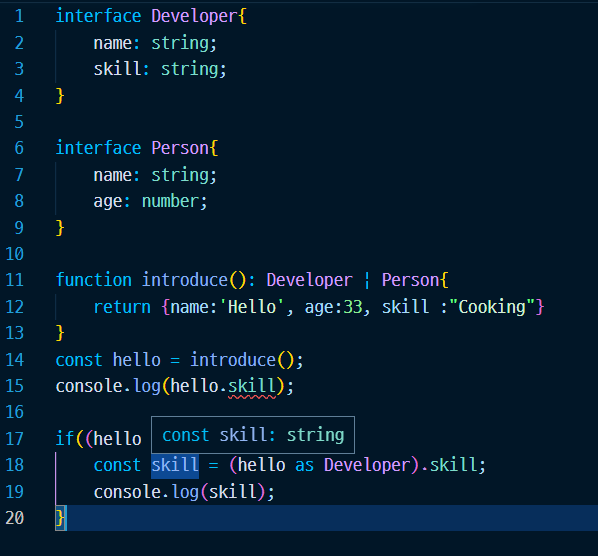
타입 단언을 통해서 유니온타입의 문제를 해결하면 가독성이 크게 떨어지는 단점이 발생한다.
interface Developer{
name: string;
skill: string;
}
interface Person{
name: string;
age: number;
}
function introduce(): Developer | Person{
return {name:'Hello', age:33, skill :"Cooking"}
}
const hello = introduce();
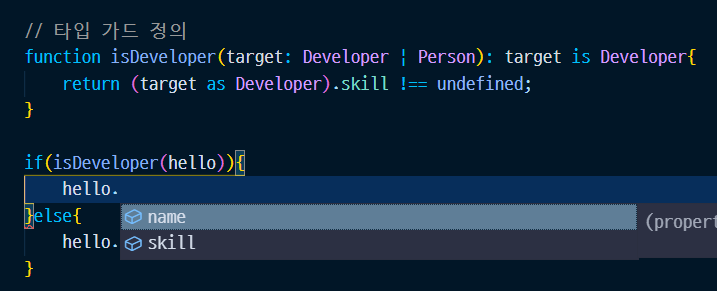
// 타입 가드 정의
function isDeveloper(target: Developer | Person): target is Developer{
return (target as Developer).skill !== undefined;
}
if(isDeveloper(hello)){
hello.
}else{
hello.age
}타입을 구분하는 isDeveloper 함수를 정의해서 target의 skill이 있을경우 isDeveloper true를 return해서 타입을 지정해준다.
www.inflearn.com/course/%ED%83%80%EC%9E%85%EC%8A%A4%ED%81%AC%EB%A6%BD%ED%8A%B8-%EC%9E%85%EB%AC%B8
해당 강의를 듣고 정리하는 내용입니다.
'JavaScript > Typescript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Typescript 입문 - 제네릭 (0) | 2020.11.29 |
|---|---|
| Typescript 입문 - 클래스 (0) | 2020.11.29 |
| Typescript 입문 - 인터페이스 / 타입 별칭 (0) | 2020.11.15 |
| Typescript 입문 - 변수와 함수 타입 정의 (0) | 2020.11.14 |
| Typescript 입문 - 타입스크립트 설치하기 (0) | 2020.11.13 |


